Cyber Security Awareness Month 2023


October is Cyber Security Awareness Month, a time for everyone to enhance their cyber security knowledge and take proactive steps to safeguard their information and devices.
This international initiative aims to raise awareness of the importance of cyber practices and and presents an ideal opportunity to take action to secure your information and devices.
- Cyber threats facing small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs)
Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are particularly susceptible to cyber security risks. Limited resources, expertise, and infrastructure, as well as a lack of awareness and training, make them vulnerable. Many inadvertently engage in risky practices like clicking on suspicious emails, using easily guessable passwords, or neglecting timely software updates. These actions can inadvertently open doors to cyber attackers.
- Cyber threats facing individuals
Individuals, much like SMBs, utilize devices (computers, mobile phones, tablets, and other internet-connected devices) and accounts (email, banking, shopping, social media, gaming, etc.) daily, leaving them exposed to a range of cyber threats in today's digital age. Some of the most prevalent threats include, but are not limited to, phishing attacks, identity theft, data breaches, and online scams.
Moraitis Consulting Joins the Cyber Security Awareness Month Campaign: Be Cyber Wise, Don't Compromise
Moraitis Consulting proudly participates in this year's Cyber Security Awareness Month campaign, themed 'Be cyber wise, don't compromise.' We strongly encourage individuals and businesses to adopt four simple steps to become cyber-wise:
-
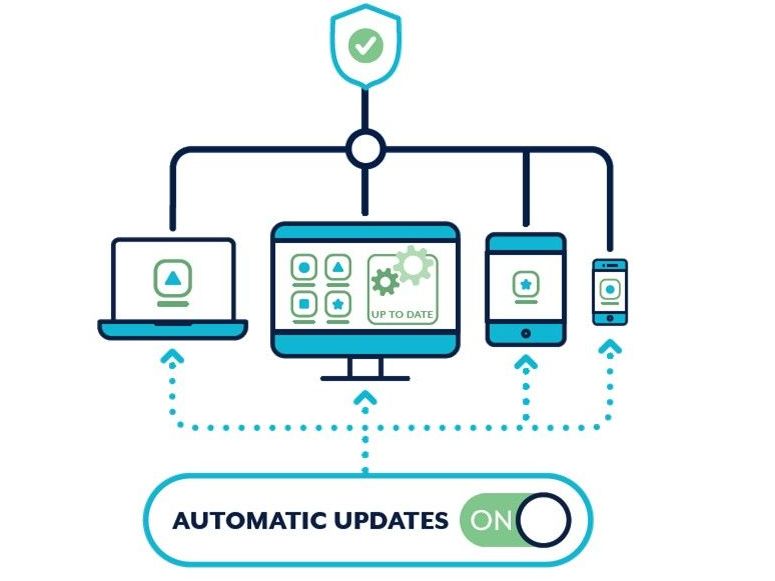
1. Update your devices regularly
What are updates?
An update is an improved version of the software (programs, apps and operating systems) you have installed on your computer and mobile devices.
- Software updates help protect your devices by fixing software ‘bugs’ (coding errors or vulnerabilities). Cybercriminals and malware can use these ‘bugs’ to access your device and steal your personal data, accounts, financial information and identity.
-New software ‘bugs’ are constantly being found and exploited by cybercriminals.
Updating the software on your devices helps protect you from cyber-attacks.
How do I set up automatic updates?
Automatic updates are a default or ‘set and forget’ setting that installs new updates as soon as they are available.
- Turn on and confirm automatic updates on all software and devices.
- How you turn on automatic updates can differ depending on the software and the device.
- Set a convenient time for automatic updates if possible, such as when you’re asleep or not typically using your device.
Your device must be powered on, plugged into power and have unused storage space. If you receive a prompt to update your device’s software you should do so as soon as possible
What if the automatic update setting is unavailable?
If the automatic update setting is unavailable, you should regularly check for and install new updates through your software or device’s settings menu.
What if my older device and software do not receive any updates?
If your device, operating system or software is too old, it may no longer be supported by the manufacturer or developer.
When products reach this ‘end of support’ stage, they will no longer receive updates. This can leave you vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Examples of products that are end of support include Windows 7 operating system and the iPhone 7.
If your device, operating system or software has reached the end of support, it is recommended to upgrade as soon as possible to stay secure.

-
2. Turn on multi-factor authentication
What is MFA?
You can use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to improve the security of your most important accounts. MFA requires you to produce a combination of two or more authentication types before granting access to an account.
-Something you know (e.g. a PIN, password or passphrase)
-Something you have (e.g. a smartcard, physical token, authenticator app, SMS or email)
-Something you are (e.g. a fingerprint, facial recognition or iris scan)
MFA makes it harder for cybercriminals to gain initial access to your account. It adds more authentication layers, requiring extra time, effort and resources to break.
How can I activate MFA to protect my most important accounts?
The steps for activating MFA are different depending on the account, device or software application. You should activate MFA now, starting with your important accounts:
- All online banking and financial accounts (e.g. your bank, PayPal)
- All email accounts (e.g. Gmail, Outlook, Hotmail, Yahoo!)
If you have a lot of email accounts, prioritise those that are linked to your online banking or other important services.
You can read more on how to turn on multi-factor authentication by searching ‘Multi-factor authentication’ or ‘MFA’ on cyber.gov.au
-
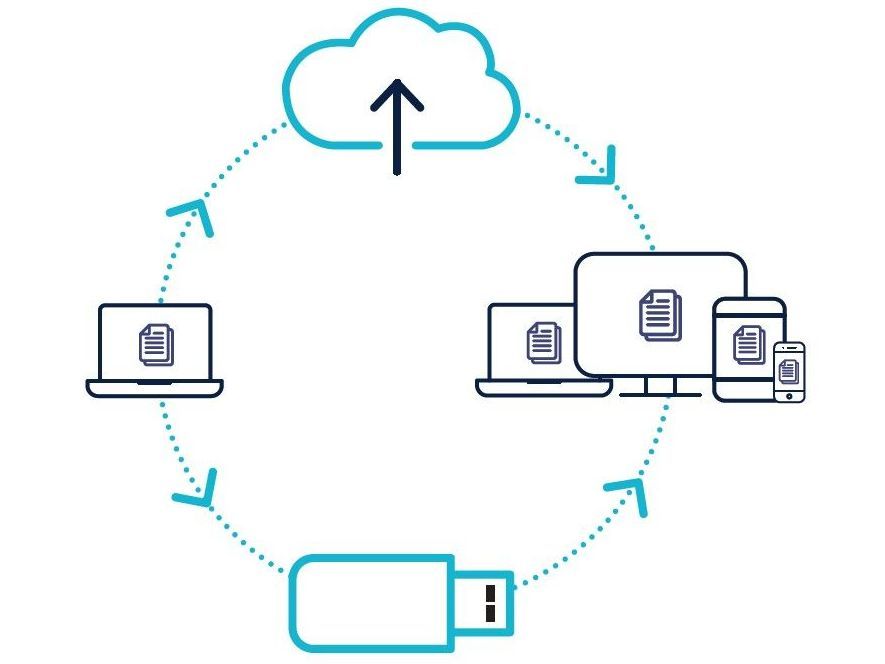
3. Backup your important files
What is a backup?
A backup is a digital copy of your information. This can include things like photos, financial information or records that you have saved to an external storage device, or to the cloud.
Backing up your information is a precautionary measure so that it can be recovered if it is ever lost, stolen or damaged.
How do I back up my devices and files?
You should regularly back up your files and devices. What that looks like, whether it is daily, weekly or monthly, is ultimately up to you.
How many times you back up could depend on the number of new files you load onto your device, the changes you make to files.
*Tip: Check your backups regularly so that you are familiar with the recovery process. Always make sure your backups are working properly.
-
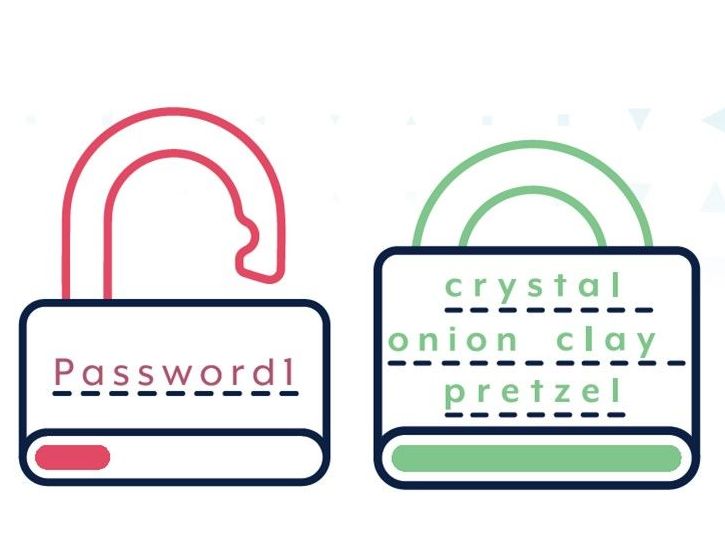
4. Use passphrases and password managers
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is one of the most effective ways to protect your accounts from cybercriminals. If MFA is not available, a unique strong passphrase can better protect your account compared to a simple password.
What is a passphrase?
A passphrase uses four or more random words as your password. For example: ‘crystal onion clay pretzel’.
-Passphrases are more secure than simple passwords.
- Passphrases are hard for cybercriminals to crack, but easy for you to remember.
How can I create a passphrase?
Create passphrases that are:
- Long: at least 14 characters long, using four or more random words. The longer your passphrase, the more secure it is.
- Unpredictable: use a random mix of four or more unrelated words. No famous phrases, quotes or lyrics.
- Unique: not re-used across multiple accounts.
If a website or service requires a complex password, including symbols, capital letters, or numbers, you can include these in your passphrase. Your passphrase should still be long, unpredictable and unique for the best security.
Which accounts should I secure with a passphrase?
If your most important accounts are not protected with MFA, change your passwords to unique strong passphrases, starting with:
- Online banking and financial accounts
- Email accounts
If you have a lot of email accounts, prioritise those that are linked to your online banking or other important services.
You can typically change your password to a unique strong passphrase through your account settings menu.
*Tip: If you struggle to remember all of your passphrases, consider using a password manager. With a password manager, you only need to remember one password, the password manager takes care of the rest. Search ‘password manager’ on cyber.gov.au for more advice.
Actions at Moraitis Consulting
At Moraitis Consulting we implement all of the above recommendations, plus we ensure our business’s policies and procedures comply with the cybersecurity framework The Essential Eight Maturity Model developed by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC).
The Essential Eight Maturity Model is designed to help organisations improve their cybersecurity posture by focusing on eight essential strategies that mitigate cyber threats. These strategies are based on the Centre for Internet Security (CIS) Controls, which are a set of best practices for securing information systems and data.
Here are the eight essential strategies outlined in the Essential Eight Maturity Model:
- Application Whitelisting: This involves only allowing approved applications to run on systems. By preventing unauthorised software from executing, organisations can reduce the risk of malware infections.
- Patch Applications: Keeping software applications up-to-date with the latest security patches helps in addressing known vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals often target outdated software to exploit security flaws.
- Configure Microsoft Office Macro Settings: Cybercriminals frequently use malicious macros in Microsoft Office documents to deliver malware. Configuring correct macro settings can prevent these malicious macros from running.
- User Application Hardening: Restricting the use of unnecessary and potentially vulnerable functionalities within applications can minimise the attack surface. By disabling unnecessary features, organisations can reduce the risk of exploitation.
- Restrict Administrative Privileges: Limiting administrative privileges ensures that only authorised users have access to critical system settings. This reduces the potential impact of malware or malicious activities.
- Patch Operating Systems: Just like patching applications, it's crucial to keep the operating systems up-to-date. Security patches are regularly released to address vulnerabilities in operating systems.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing accounts or systems. This significantly enhances security, especially in case of stolen or weak passwords.
- Daily Backups: Regularly backing up important data is essential. In the event of a ransomware attack or data loss, having up-to-date backups ensures that critical information can be restored without paying a ransom.
The Essential Eight Maturity Model is not a one-size-fits-all approach. SMBs are encouraged to assess their specific cybersecurity risks, capabilities, and resources, and tailor the implementation of these strategies according to their needs. By adopting these essential strategies, at Moraitis Consulting we can enhance our cybersecurity defences against a wide range of cyber threats.
Additional Recommended Actions
-
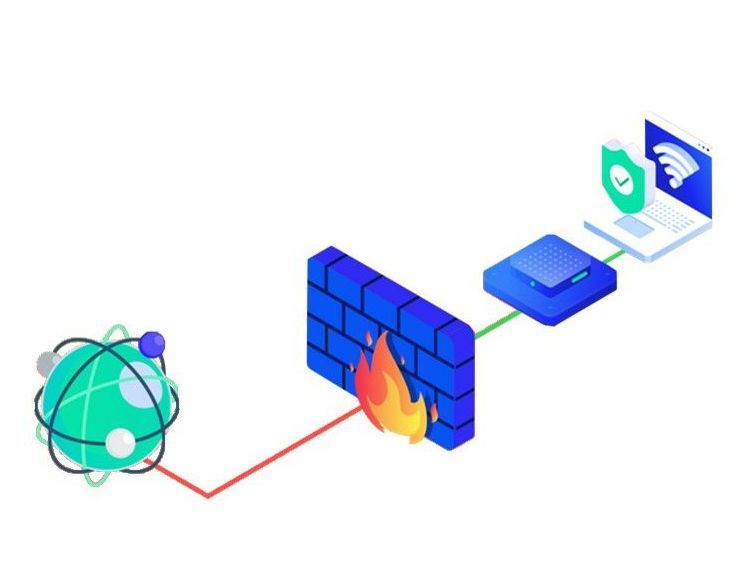
5. Secure your Internet connections with Firewalls
A firewall is a security device that protects your network from unauthorised access to private data. Firewalls also secure computers from malicious software, creating a barrier between secured internal networks and untrusted outside networks.
What is the role of firewalls in cybersecurity?
Firewalls play a crucial role in cybersecurity by acting as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. They function as a security device or software that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
How does a firewall work?
Firewalls typically welcome incoming connections that are allowed to access a network. The security systems will allow or block data packets based on existing security rules. Firewalls build checkpoints that filter web traffic. These systems let you review and act upon rogue network traffic before the attacked network experiences any adverse effects.
With a dependable firewall in place, only trusted sources and IP addresses can access your client’s systems. Some firewalls can also monitor audit logs to find connections and traffic that have gotten through.
Use firewalls to gate the borders of private networks and the host devices. Ensure that you include robust firewalls when setting up user access controls. You can set up these barriers on user computers or dedicated computers on the network.
Types of firewalls
Firewalls could either be software or hardware devices. Software firewalls are computer programs that you can install on user devices. They monitor and regulate network traffic through port numbers and applications. Hardware firewalls are the equipment you establish between your client’s network and the gateway.

-
6. Use Antivirus software
Security software such as anti-virus and ransomware protection can help protect your devices.
Anti-virus software can be set up to regularly scan for suspicious files and programs. When a threat is found, you will receive an alert and the suspicious file will be quarantined or removed.
Many small businesses can use Windows Security to protect themselves from viruses and malware. Windows Security is built-in to Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices and includes free virus and threat protection. You can also use it to turn on ransomware protection features on your device.
For more information regarding Antivirus visit ACSC's website.
Cybercrime on the Rise: Take Action
Cybercrime reports are increasing, but by taking these simple steps, everyone can play a part in making Australia the most secure place to connect online. The Australian Cyber Security Centre's Annual Threat
Report for 2021-22 revealed a 13% rise in reported cybercrimes compared to the previous year. Frauds, online shopping, and online banking comprised over half of all reports.
If you are concerned about your cyber security, explore resources and guidance from the Australian Cyber Security Centre, where you can find resources and valuable information about how to be cyber-safe.
For comprehensive cyber security assistance, feel free to contact us. Moraitis Consulting is here to support your cyber security needs.
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.







Your Trusted Partner

Head Office
Level 4
66 Smith Street
Darwin, N.T. 0800
PO Box 4580
Darwin NT 0800
Qld Office
The Hive
Level 1
Tower 2
55 Plaza Parade
Maroochydore QLD 4558
Privacy - ©2025 Moraitis Consulting Pty Ltd, All rights reserved.

